Configuring Smart Client for Certificate Authentication
Configuring Smart Client for Certificate Authentication
Step 1: Configure the computer where Smart Client is installed.
Install the client security certificate for the current user:
To start this process, you will need a personal client certificate and password for the private key. Your system administrator will supply these to you.
- Start your web browser.
- Import the personal certificate into your web browser, using commands such as Tools / Internet Options / Content / Certificates / Import . Select the file with the personal client certificate. You will need to enter a password for the private key. Accept all defaults, and click “Finish”.
- The system will display a message that the import was successful.
Configure your Web Browser
If there is a single certificate suitable for the particular request, you can configure your browser to use it automatically.
-
Start your browser. In
Tools > Internet Options > Security > Custom Level
, enable “Don't prompt for client certificate selection when only one certificate exists” option.
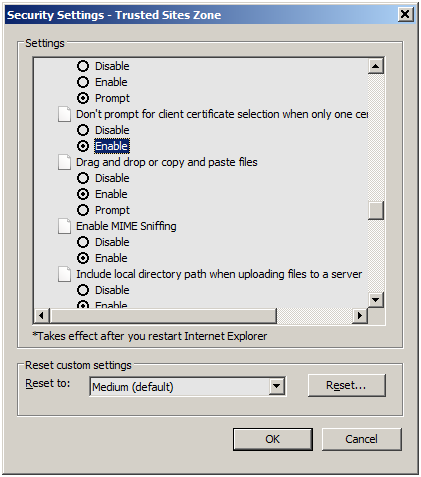
-
In
Tools > Internet Options > Security > Trusted
sites, add the URL of your server to the trusted zone.

- Close Internet Explorer.
- Start Internet Explorer.
- Enter the URL of the Web Central server, for example: https://ubuntu/archibus/. Web Central will start.
Step 2: Use the personal security certificate in Smart Client
- Start Smart Client
- Click on the “Sign In” button.
- On the “Sign In” form, click on “Select Server” button.
- On the “Select Server” form, enter the URL of the server which is configured to require client certificate.
- Check “Use personal security certificate” option.
- Click on “Select” button, and select the security certificate.
- Click on OK” and the “Select Server” form will close.
- Click on OK, and the “Sign In” form will close.
Technical details
When the user signs in to Smart Client, the Smart Client Web Services present that certificate to the server for the client authentication.
The option to use certificate client authentication in Smart Client is enabled only if the user enters a URL address on the “Select Server” form.
The Internet Explorer settings control the certificate that will be used by the embedded Web Browser control. The embedded Web Browser is used when user clicks on “Web Central” button or loads Web Central view in the Navigator.
The user can set Internet Explorer to automatically use a "suitable" certificate if it finds that one exists on the local workstation, via Tools > Internet Options > Security > Custom Level-> Don't prompt for client certificate selection when only one certificate exists .
If this setting is not used, Internet Explorer prompts for the certificate the first time the user tries to access a Web resource protected by certificate security.
If there is more than one certificate on the workstation, the user may select one certificate for the Smart Client and a different one for Internet Explorer (and thereby the embedded Web Browser). In this case, in theory, they could log into Archibus as two different identities (e.g. "ABERNATHY" for the Smart Client and "CARLO" for embedded Web Browser).
However, this "dual identity" condition is unlikely, as the reason sites authorize certificate authorities and issue personal certificates to individual users is to identify that user in particular person. If they have different identities, it's for a deliberate reason, and they aren't likely to be authorized to use two different personal certificates against the same Web resource (in this case proxy server for Archibus).
See also: Troubleshooting Archibus Smart Client authentication
References
1. http://blogs.msdn.com/b/ieinternals/...on-prompt.aspx
2. http://support.microsoft.com/kb/933430
The server sends a list of trusted certificate authorities to the client.
This list of trusted certificate authorities represents the authorities from which the server can accept a client certificate. To be authenticated by the server, the client must have a certificate that is present in the chain of certificates to a root certificate from the server's list.
Schannel creates the list of trusted certificate authorities by searching the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store on the local computer. Every certificate that is trusted for client authentication purposes is added to the list.
